Describe the Structure of the Skin
Epidermis As the outermost skin layer that we see and touch the epidermis performs skins primary function acting as a barrier to protect us from toxins bacteria and fluid loss. The skin itself has two major tissue layersthe epidermis and the dermis.

Structure And Function Of Skin Biology For Majors Ii
Anatomy of the Skin.

. These structures embryologically originate from the epidermis and can extend. This is the layer of skin that we can see it has the thickest layer which can be found on the soles of the feet and palms of the hands thinnest layer on the eyelids and nipples. This layer of skin contains many cells each called a keratinocyte a keratin-producing cell found in the skinKeratin is the structural protein that lends durability and water impermeability to skin hair and nails.
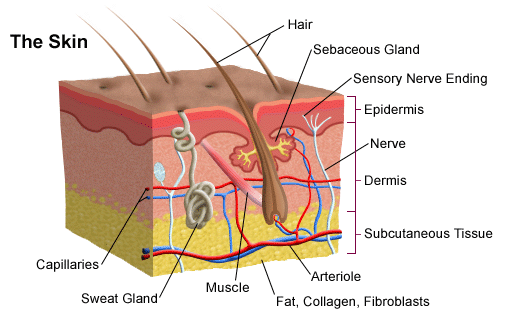
There are three main layers of skin. Getting Under the Skin. The skin has three layers.
Explain the role of the integumentary system in maintaining homeostasis. It protects the body against physical injuries temperature regulation sunlight infection stores water fat and plays a key role in metabolism including vitamin D among other functions. Accessory structures of the skin include hair nails sweat glands and sebaceous glands.
Not surprisingly the skin has a complex architecture that can vary depending on body location Figure 1. Beneath the epidermis is the dermis layer. Explain the Features of the Hypo Dermis.
This subcutaneous layer is made up of. It consists of papillae which form finger-like projections. The dermis beneath the epidermis contains tough connective tissue.
Describe the structure of each layer of skin of the hand and how it is related to its specific function at that location. The Epidermis The epidermis is the top most layer of the skin. Examine the conceptual relationship between the structure and function of the integumentary system.
Describe the structure and functions of the layers of the epidermis Be aware of the functions of melanocytes and Langerhans cells List the components and functions of a pilosebaceous unit Distinguish between eccrine and apocrine sweat glands describe the major functions of the skin - protection sensation and homeostatic functions. The epidermis the outermost layer of skin provides a waterproof barrier and creates our skin tone. Beneath the surface of the skin are nerves nerve endings glands hair follicles and.
The skin is a vital organ that covers the entire outside of the body forming a protective barrier against pathogens and injuries from the environment. The skins structure is made up of an intricate network which serves as the bodys initial barrier against pathogens UV light and chemicals and mechanical injury. Covering the entire outside of the body it is about 2 mm thick and weighs approximately six pounds.
Describe the condition of the nails and what disease or disorder it may point to. Describe the age-related changes that occur to the integumentary system. Describe how the structure of skin appendages present at your chosen location is adapted for its given function.
Skin has three layers. The skin is the largest organ in the body making up 12 15 of body weight and with a surface area of 1 2m 2. Describe the structure and function of sweat glands and sebaceous glands.
The epidermis is the outermost layer. The deepest layer of skin. Accessory structures of the skin include hair nails sweat glands and sebaceous glands.
Name at least 3 diseases that might be suspected based on the look of ones nails. - lies beneath dermis. This article gives an overview of the structure and functions of the skin.
- contains nerve endings that. Structure of the skin. Choose a skin disorder and describe how the structure of the skin is affected by the disorder.
There are 3 distinct regions in the skin. - adipose tissue fatty tissue cushions and insulates. Skin conditions are visible in this skin- beauty- and image-conscious society the way patients are accepted by other people is an important consideration for nurses.
The cells in this layer are called keratinocytes. What are the 3 main layers of skin. The skin has three basic layers the epidermis the dermis and the hypodermis.
The skin has three layers. - anchors the skin to underlying structures. The skin consists of two layers EPIDERMIS and DERMIS Epidermis.
The basic structure of hair is medulla cortex and cuticle. The skin consists of three main layers epidermis upper or outer layer dermis lower or inner layer and subcutaneous tissue. The skin is the bodys largest organ.
The skin is the largest organ in the body. The epidermis is the outermost layer of skin comprised of several sublayers. Structure Of Skin Epidermis.
Also include the disease signs symptoms and treatment. Describe the structure of the joints and associated bones and other. Use correct terminology related to.
These structures embryologically originate from the epidermis and can extend. The three main skin layers are the epidermis dermis and subcutis. The total skin surface of an adult ranges from 12-20 square feet.
It is a waterproof barrier that gives skin its tone. It is made up of three layers the epidermis dermis and the hypodermis all three of which vary significantly in their anatomy and function. Part 2 will provide an overview of the accessory structures of the skin and their functions.
From outermost inward they are the epidermis dermis and subcutis hypodermis. The skin is the largest organ of the body it covers the whole body and they are water resistant. The basic structure of skin is epidermis dermis and hypodermis.
The middle layer which consists of two parts known as the papillary dermis thin upper layer and the reticular dermis thick lower layer Subcutaneous tissue. It is the outermost layer of the skin. In terms of chemical composition the skin is about 70 water 25 protein and 2 lipids.
Describe the layers of the skin and associated accessory structures. The outermost layer which contains five sub-layers. Describe the structure and function of sweat glands and sebaceous glands.
The skin consists of three main layers - Epidermis Dermis and Subcutaneous tissue.

Skin Diagram And Information About Your Skin Skin Anatomy Integumentary System Psoriasis Skin
No comments for "Describe the Structure of the Skin"
Post a Comment